So as to stay upright, living animals depend on their perception of senses; in people, balance is kept up utilizing a mix of liquids as a part of the internal ear, vision, and something many refer to as proprioception – the body’s feeling of where it is in space. It’s a finely tuned framework and in the same way as other organic frameworks, hard to imitate in robots.
Rather, robots utilize a bit of innovation called an accelerometer. This depends on the power of gravity to tell the machine where the focal point of the Earth is in respect to its own position; it is upright when its lower side is confronting that heading. Thusly, flying robots have the capacity to stay level with the skyline, regardless of how uneven the territory, since it is not depending on geology, which is uneven, but rather gravity, which is even.
Albeit there is proof to recommend that bugs depend on gravity for balance, they likewise depend intensely on vision. It’s this sight-based sense that has roused scientists Fabien Expert and Franck Ruffierat the Aix-Marseilles University’s Institut des Sciences du Mouvement Etienne-Jules Marey to construct a honey bee motivated flying robot.
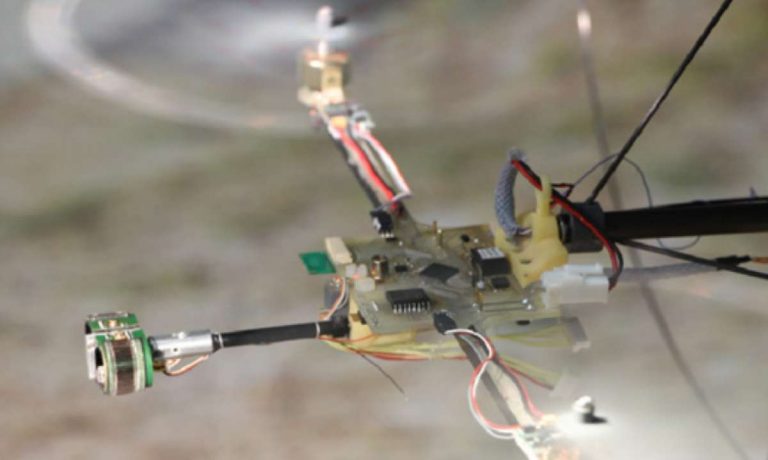
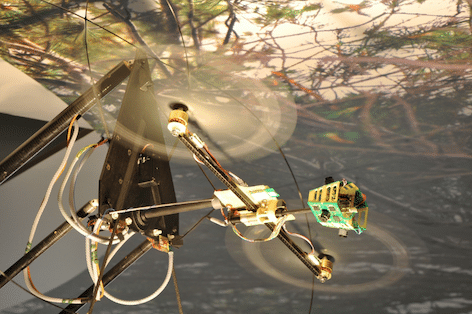
The BeeRotor which weighs 80g and is 47cm in dimensions is a fastened robot that can fly along a passage with uneven moving dividers utilizing only its optic stream sensors – measuring neither velocity nor height, however basically outwardly gaging its position.Optic stream is utilized vigorously by flying creepy crawlies. As something travels through the scene, the range before the moving item stays genuinely stable; in any case, to either side, it goes by progressively speedier, coming to a greatest pace when opposite to the way of the article.
To duplicate bugs’ capacity to utilize optic stream, the scientists furnished BeeRotor with 24 photodiodes circulated at the top and base of its eye, which permits the robot to recognize complexities and movement in nature around it. At the point when the pace at which a component of the view moves starting with one pixel then onto the next increments, the robot has the capacity to confirm that possibly its speed is accelerating, or its separation from that element is diminishing.
Three observations then make utilization of the information from the optic sensors to arrange the robot. The main changes the robot’s height because of visual information with the goal that it takes after either the floor or the roof of the passage. The second circle controls the robot’s rate in light of the span of the passage. The third settles the “eye” because of the slant, so that it generally has the best conceivable field of perspective, maintaining a strategic distance from steeply inclining snags without an accelerometer.
The achievement of the trial, the specialists accept, advances a conceivable theory clarifying how creepy crawlies could arrange themselves with no feeling of gravity – by utilizing an input circles like those utilized by BeeRotor.
In spite of the fact that it is more probable that, as different creatures, creepy crawlies utilize a mix of faculties to focus introduction, the examination likewise shows another system for introduction that could go about as a lightweight safeguard or corresponding framework to the accelerometer.